ICU Setup At Homes
ICU Setup at home is serious undertaking and requires careful planning and consideration. Setting up an ICU at home involves creating a space equipped to provide intensive care for patients who require close monitoring and medical intervention. This typically includes medical equipment such as ventilators, cardiac monitors, infusion pumps, and oxygen supplies, as well as trained medical personnel to provide care. It’s crucial to ensure proper training, resources, and support when considering such a setup.
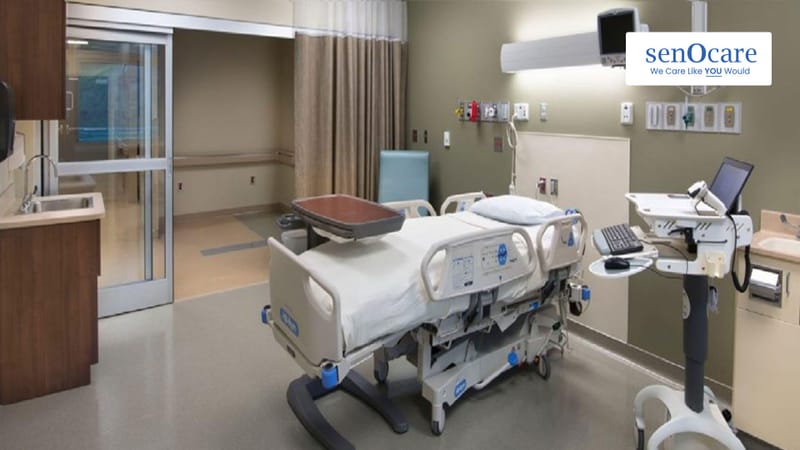
IMPORTANCE OF HOME ICU SETUP
COMFORT AND FAMILIARITY : Patients often feel more comfortable and secure in their own homes, which can positively impact their emotional well-being and recovery process.
REDUCED RISK OF INFECTIONS : Home environments typically have fewer pathogens compared to hospitals, reducing the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
COST- EFFECTIVENESS : Managing critical care at home can be more cost-effective than prolonged hospital stays, especially for long-term care needs.
PERSONALIZED CARE : Patients receive individualized attention and care plans tailored to their specific needs, enhancing treatment effectiveness and outcomes.
IMPROVED QUALITY OF LIFE : Being at home allows patients to maintain a sense of normalcy, engage with family members, and participate in familiar activities, which can improve their overall quality of life.
FLEXIBILITY AND AUTONOMY : Home ICU setups offer greater flexibility in scheduling visits from healthcare providers and allow patients more autonomy in decision-making regarding their care.
FAMILY INVOLVEMENT : Family members can actively participate in caregiving and support, fostering a stronger support system and potentially improving patient outcomes.
CONTINUITY OF CARE : Transitioning from hospital to home ICU ensures continuity of care, with the ability to seamlessly integrate medical treatment.
ALLOCATION : Home ICU setups helps alleviate strain on hospital resources by providing critical care outside of traditional healthcare facilities, freeing up beds for patients with acute needs.
TYPES OF ICU :
Medical ICU (MICU)
The Medical Intensive Care Unit(MICU) is a specialized department in hospitals dedicated to the care of critically ill patients with severe medical condition. It’s equipped with advanced monitoring and life-support equipment to provide intensive medical care and support to patients who require close monitoring and treatment.
Surgical ICU (SICU)
The Surgical Intensive Care Unit (SICU) is similar to the Medical ICU but focuses on caring for critically ill patients who have undergone surgical procedures or trauma. It provides specialized care tailored to the needs of post-operative patients, including monitoring vital signs, managing pain, preventing complications, and facilitating recovery.
Cardiac ICU (CICU)
The Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides comprehensive care for patients with critical cardiac conditions.
Neurological ICU (NICU)
The Neurological Intensive Care Unit (NICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that focuses on the care of critically ill patients with neurological conditions, such as strokes, traumatic brain injuries, seizures, or neurosurgical procedures.
Pediatric ICU (PICU)
The Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides intensive care of critically ill infants, children and adolescents.
Neonatal ICU (NICU)
The Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) is a specialized department within a hospital that provides intensive medical care to newborn infants, particularly those who are premature, have low birth weight, or have medical complications.
Trauma ICU
The Trauma Intensive Care Unit (TICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides intensive care for patients who have sustained severe traumatic injuries, such as those from accidents, falls, or violence.
Burn ICU
The Burn Intensive Care Unit (BICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides comprehensive care for patients with severe burns.
Cardiothoracic ICU
The Cardiothoracic Intensive Care Unit (CICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides intensive care for patients who have undergone cardiothoracic surgery, such as heart or lung surgeries.
Oncological ICU
The Oncological Intensive Care Unit (OICU) is a specialized unit within a hospital that provides intensive care for patients with cancer who require critical care support.
EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES :
· Ventilator or BiPAP machine: Ventilator or BiPAP machines serve different purposes. Ventilators are primarily used for patients who cannot breathe on their own, while BiPAP machines provide non-invasive ventilation support for conditions like sleep apnea or respiratory issues.
· Oxygen concentrator and backup oxygen tanks: Oxygen concentrators extract oxygen from the surrounding air, providing a continuous flow of oxygen. They’re convenient for home use.
· Pulse oximeter: A pulse oximeter is a small, portable device used to measure the oxygen saturation level in the blood and the heart rate.
· Blood pressure monitor: A blood pressure monitor is a device used to measure blood pressure, typically consisting of an inflatable cuff placed around the upper arm and a gauge or digital display that shows the pressure readings.
· Suction machine: A suction machine is a medical device used to remove fluids, gases, or debris from a patient’s body during surgery or in cases where the body is unable to do so effectively on its own.
· Nebulizer: A nebulizer is a device used to administer medication in the form of a mist that is inhaled into the lungs.
· Thermometer: A thermometer is a device used to measure temperature.
· Examination table: An examination table, also known as a medical examination table or exam table, is a piece of furniture used in healthcare settings for patients to sit or lie on during medical examinations or procedures.
· Diagnostic imaging equipment (e.g., X-ray, ultrasound): Diagnostic imaging equipment refers to a range of medical devices used to create visual representations of the internal structures of the body for diagnostic purposes.
· Scalpel: A scalpel is a small, sharp knife used in surgical procedures to make precise incisions or cuts in tissue.
· Suture kit: A suture kit is a collection of medical instruments and supplies used for closing wounds or surgical incisions by stitching them together with sutures(also known as stitches).
· Syringe and needles: Syringe and needles are essential medical devices used for administering medications, vaccines, and fluids, as well as for drawing blood or other fluids from the body.
SUPPLIES NEEDED :
Oxygen tubing and masks: Oxygen tubing and masks are essential medical equipment used to deliver oxygen to patients who have difficulty breathing on their own.
IV fluids and administration sets: IV(intravenous) fluids and administration sets are crucial in medical settings for delivering fluids, medications, and nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
Medications (prescribed by a doctor): Medications encompass a vast range of substances used to prevent, treat, or manage various medical conditions.
Wound care supplies: Wound care supplies are essential tools used to clean, dress, and protect wounds to facilitate healing and prevent infection.
Disposable gloves, masks, and gowns: These are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) used in healthcare settings to prevent the transmission of infectious agents between patients and healthcare providers.
Safety measures: Safety measures are crucial to ensure the well-being of patients, healthcare workers, and visitors.
ELECTRICAL SAFETY:
Proper grounding of equipment: It is crucial for patient safety and to prevent electrical hazards. All electrical equipment should be grounded according to manufacturer guidelines and hospital protocols.
Use of surge protectors: Surge protectors can be used to safeguard sensitive medical equipment from power surges and spikes, which could otherwise damage the devices or compromise patient care.
Keeping cords organized and away from walkways: It is in essential in ICU settings to prevent trip hazards and ensure easy access for healthcare professionals.
INFECTION CONTROL :
Hand hygiene protocols: Healthcare workers are required to wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand sanitizers before and after patient contact, after removing gloves, and whenever hands are visibly soiled.
Regular disinfection of surfaces and equipment: This is to minimize the risk of healthcare-associated infections(HAIs).
Proper disposal of medical waste: Proper disposal of medical waste in ICU settings is critical to prevent the spread of infections and protect the environment.
EMERGENCY PREPAREDNESS :
- Fire extinguisher placement and usage
- Emergency contact list (medical professionals, ambulance services)
- Family members trained in CPR and basic first aid
- Key responsibilities of Nurse at ICU at Home
- Monitoring and Documentation
VITAL SIGNS MONITORING SCHEDULE
Frequency of checking pulse, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and temperature
Recording observations accurately
DOCUMENTING INTERVENTIONS AND RESPONSES
Keeping a log of medications administered, changes in condition, and any incidents
Sharing information with healthcare providers during consultations or emergencies
Emotional and Psychological Support
COPING STRATEGIES FOR PATIENTS AND CARE-GIVERS
· Stress management techniques: Deep breathing exercises, meditation or mindfulness practices, regular physical activity, prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals, etc.
· Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups: In ICU settings , seeking support from friends, family, or support groups is crucial for both patients and their loved ones. It can provide emotional comfort, information, and guidance during a challenging time.
· Encouraging open communication about feeling and concerns: Encouraging open communication about feelings and concerns is vital, especially in stressful situations like being in the ICU. It allows patients, and their loved ones to share their worries, fears, and hopes, fostering a sense of connection and understanding.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, open communication about feelings and concerns is essential, particularly in challenging circumstances such as being in the ICU.
Summary:
In an ICU guide, key points typically cover patient monitoring, ventilator management, medication administration, infection control, nutrition support, and communication strategies with patient and families.
Encouragement to seek professional advice and assistance
SENOCARE provides all kinds of facilities right at home, whether related to health or travel, electricity, or any other task. For those elders who can’t go outside, medical services are provided at home, and by staying connected with them, every requirement is fulfilled. Senocare ensures you never feel alone and pays complete attention to your health, be it physical or mental, giving you a homely feel.