Is Physiotherapy Good for Back Pain?
Back pain is a common issue that affects millions of people worldwide impacting their day to day tasks. This article explores the effectiveness of physiotherapy for addressing lower back pain, exploring its procedures, causes, and considerations for those seeking this non-invasive treatment approach.(1)
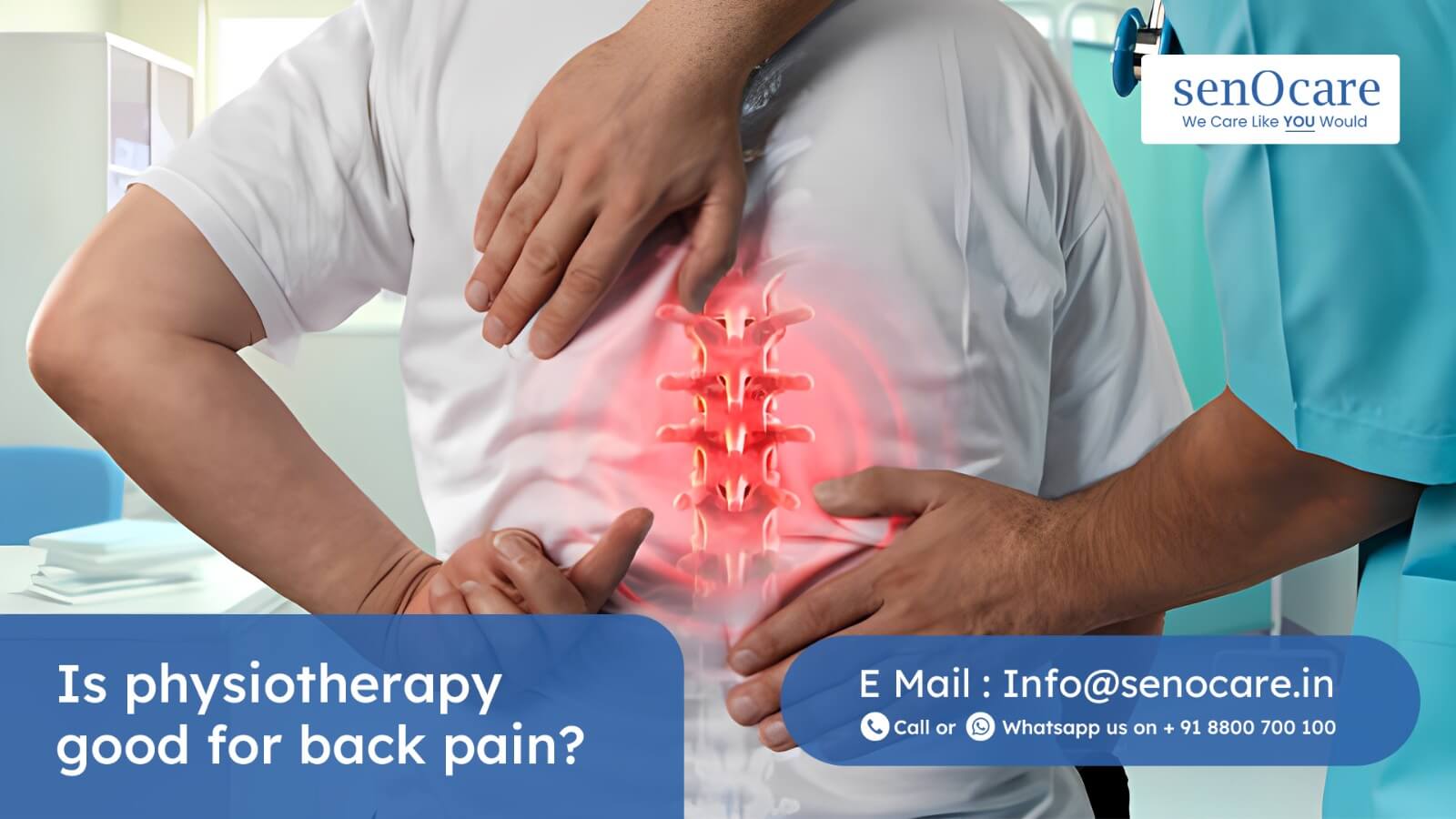
About Physiotherapy for Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy is a holistic healthcare approach that addresses musculoskeletal issues including lower back pain through targeted exercises and interventions to improve mobility, reduce pain, and enhance overall well-being(2)
What Are the Causes of Back Pain?
Understanding the causes of back pain is crucial for effective treatment. The common causes of back pain include poor posture, muscle strain, herniated discs, and underlying health conditions. However certain other less common conditions such as spinal tumors, burst fractures of vertebrae’s and tuberculosis of spine can also lead to severe back pain. Physiotherapy targets the root causes rather than merely alleviating symptoms, making it a comprehensive and sustainable approach.
- posture
- Muscle strain
- Herniated discs
- Underlying health conditions
- Spinal tumors
- Burst fractures of vertebrae’s
- Tuberculosis of spine
Find a Physiotherapist
Choosing the right physiotherapist is immensely important the success of your treatment. Contacting legitimate professionals with experience and expertise helps in successfully treating your specific condition. Senocare’s specialized services provide you with highly qualified physiotherapist right at your doorstep.
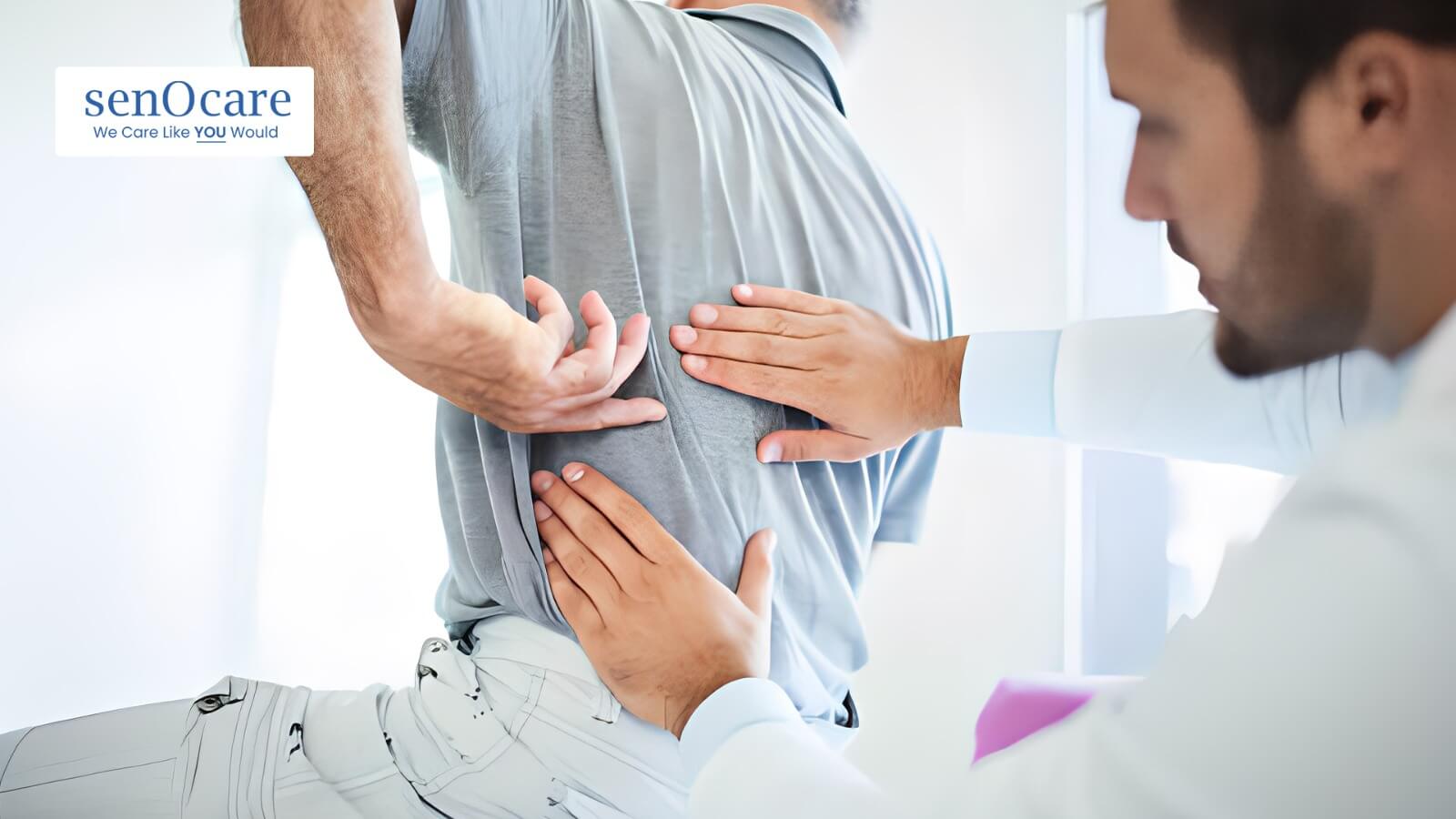

Physiotherapy Procedure
Physiotherapy involves two primary forms of treatment: passive and active.
Passive physiotherapy
This includes interventions where your physiotherapist will treat you without active participation. These include deep tissue massages, dry needling, cupping therapy heat therapy, or ultrasound. This is generally done in the acute phase of treatment to promote healing of the body.
Active physiotherapy
This on the other hand, involves exercises and stretches that the patient actively performs to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. These are done in the later phase of treatment to develop strength endurance and prevent reoccurrence of the pain.(3)
How Long Does it Take for Physiotherapy to Work for Back Pain?
The duration of physiotherapy effectiveness varies from person to person and also on the root cause of pain. Factors like the severity of the condition, consistency in attending sessions, and adherence to prescribed exercises influence the speed of recovery influence the duration and effectiveness of treatment. While some individuals experience relief after a few sessions, others may require a more extended treatment plan.
When Should You See a Physiotherapist for Back Pain?
If you experience persistent or worsening back pain, it’s advisable to consult a physiotherapist promptly as early intervention is crucial in effective management of the pain. Timely treatment can prevent the issue from escalating and improve the likelihood of a successful recovery.
Which Therapy Is Best for Back Pain?
The most effective therapy depends on the specific causes of your back pain. A skilled physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment and tailor a treatment plan that may involve a combination of passive and active therapies. This personalized approach ensures targeted and optimal results.
What Is the Best Time for Physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy can be beneficial at any stage of back pain. However, early intervention often yields better outcomes. Don’t delay seeking treatment, especially if the pain is impacting your daily activities. Starting physiotherapy promptly can prevent the development of chronic issues and continuing treatment regularly helps prevent the pain from reoccurring.
Exercise and Staying Active
Regular exercise plays a pivotal role in managing and preventing back pain. Physiotherapists often recommend exercises that focus on strengthening core muscles, improving posture, and increasing flexibility. Common exercises include core muscle activation, spinal mobility exercises, gentle stretches, pelvic tilts, and low-impact aerobic activities like walking or swimming.
Aftercare for Physiotherapy
After completing a physiotherapy program, it’s essential to maintain a proactive approach to prevent the recurrence of back pain. Continue with the prescribed exercises which need to be progressed from time to time and incorporated into your regular routine. Practice good posture, ergonomics, and stay active to support the gains achieved through physiotherapy. Regular follow-ups with your physiotherapist may be recommended for ongoing guidance and support.
In conclusion, physiotherapy emerges as a valuable and effective option for individuals grappling with lower back pain. By understanding its procedures, seeking timely intervention, and incorporating aftercare practices, individuals can not only find relief but also enhance their overall well-being, paving the way for a healthier and more active life.
Bibliography
1. Meucci RD, Fassa AG, Faria NM. Prevalence of chronic low back pain: systematic review. Rev Saude Publica. 2015;49:1. doi: 10.1590/S0034-8910.2015049005874. Epub 2015 Oct 20. PMID: 26487293; PMCID: PMC4603263.
2. George SZ, Fritz JM, Silfies SP, Schneider MJ, Beneciuk JM, Lentz TA, Gilliam JR, Hendren S, Norman KS. Interventions for the Management of Acute and Chronic Low Back Pain: Revision 2021. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2021 Nov;51(11):CPG1-CPG60. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2021.0304. PMID: 34719942; PMCID: PMC10508241.
3. Hlaing SS, Puntumetakul R, Khine EE, Boucaut R. Effects of core stabilization exercise and strengthening exercise on proprioception, balance, muscle thickness and pain related outcomes in patients with subacute nonspecific low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021 Nov 30;22(1):998. doi: 10.1186/s12891-021-04858-6. PMID: 34847915; PMCID: PMC8630919.